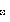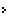Colossal, surreal and beautiful, the mighty edifice of Jama Masjid is impressive enough to make you sit up and take notice of this sprawling edifice. The last architectural venture of Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan, Jama Masjid holds the reputation of being the biggest mosque in India. Located in Delhi, besides the famous Red Fort, Jama Masjid derives its name from the word 'Jummah', which refers to the ritualistic congregational prayer that Muslims observe every Friday. The mosque boasts of huge carved doorways with entrances in both northern and southern direction. Made of white marble and sandstone, this sprawling mosque can accommodate around 25000 devotees at a time. A fine example of Mughal artisanship, this magnificent edifice is a beautiful amalgamation of Hindu and Islamic architectural designs. In the month of Ramzan and on every Friday, devotees flock here to offer 'namaz'. Inside the mosque, you will find prized relics of Islam like a copy of Holy Quran written on the skin of deer, a red beard hair of Prophet Muhammad, his footprints and slippers.
Colossal, surreal and beautiful, the mighty edifice of Jama Masjid is impressive enough to make you sit up and take notice of this sprawling edifice. The last architectural venture of Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan, Jama Masjid holds the reputation of being the biggest mosque in India. Located in Delhi, besides the famous Red Fort, Jama Masjid derives its name from the word 'Jummah', which refers to the ritualistic congregational prayer that Muslims observe every Friday. The mosque boasts of huge carved doorways with entrances in both northern and southern direction. Made of white marble and sandstone, this sprawling mosque can accommodate around 25000 devotees at a time. A fine example of Mughal artisanship, this magnificent edifice is a beautiful amalgamation of Hindu and Islamic architectural designs. In the month of Ramzan and on every Friday, devotees flock here to offer 'namaz'. Inside the mosque, you will find prized relics of Islam like a copy of Holy Quran written on the skin of deer, a red beard hair of Prophet Muhammad, his footprints and slippers.Brief History
This mosque was built in 1628 A.D. by more than five thousand workers, who pegged away for seven years to complete this unique edifice. The edifice was built around a whopping budget of ten lakh rupees and was constructed under the supervision of Shah Jahan's Prime Minister, Saadullah Khan. The mosque is built in a way that you can enter the main prayer hall from any of the three directions - north, south and east. However, the main entrance is on the eastern side, opposite to the Red Fort. Formerly, there used to be a madrasah near the southern part of the mosque, which was demolished during the Indian Independence struggle. Three projecting porticoes separate the minarets of the mosque and are surmounted by open twelve-sided domed pavilions. In addition, there are four small minarets on the rear side of the mosque and a white marble entrance carved with calligraphies in black marble.
Major Attractions
Jama Masjid is a head-turner for more reasons than one. This iconic architecture, posited in one of the busiest touristy areas in Delhi, is best known for its dynamic manifestations. From the transliterations of the Holy Quran to exquisitely designed pillars to beautifully carved arches, Jama Masjid is a visual treat for the eyes. The main prayer hall boasts of beautiful curves and engraved marble domes. The main tower of the mosque has five distinct storeys, two minarets, and four foundation pillars carved with complex designs. Another thing to observe and admire is the high ground construction of the mosque and the wide and elevated steps. Furthermore, the flooring of the mosque is the center of attraction, which looks like a prayer mat. The ideal time to visit the mosque is from October to March as the temperature is moderate then.
How To Reach The Shrine
One can easily reach the mosque from ISBT, Connaught Place and ITO. To reach Delhi, one can choose the option according to the expenses.
By Air: Indira Gandhi International Airport is located 23 km southwest to Central Delhi and the domestic terminal is located in Palam, which is 5 km away from the international terminal. Once you arrive at the airport, you can hire cabs or avail the tourist buses to reach Jama Masjid.
By Train:
Delhi is the main center of the Indian Railways network. The capital has two major railway stations - New Delhi and Old Delhi. New Delhi station is at a walking distance from Connaught Place whereas Old Delhi station is about 7 km away from Connaught Place.
By Road:
There are buses available from Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh and Punjab. One can also avail the private taxis to reach Delhi.
Jama Masjid, the historical mosque, attracts people from all corners of the globe. This mosque is one of the striking examples of the exceptional and admirable works of the Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan.